Sungkyunkwan UniversityNanoEnergy & NanoSensors Laboratory Lab
Research
Research Field
Research Field
Nanoplasmonics

Nanoplasmonics
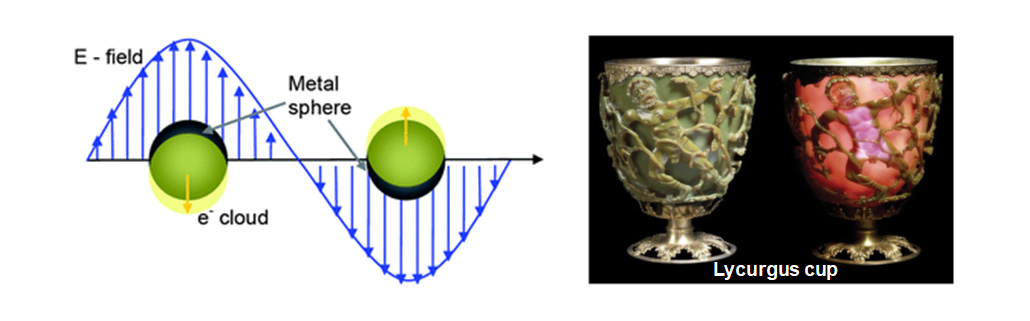
Plasmons are the oscillations of free electrons at a metal surface by external photons. Nanoplasmonics is a plasmonic effect at nano-sized noble metal in which localized surface plamson resoncance (LSPR) occurs. Noble-metal nanoparticles with sizes smaller than the wavelength of visible light show strong resonances for light scattering and absorption, due to the excitation of localized surface plasmons. Its resonance frequency is strongly dependent on particle shape and dielectric environment, which enable expressing of its "color" throughout the visible and into the near-infrared(IR) regime of the spectrum, while keeping particle size well below 100nm.
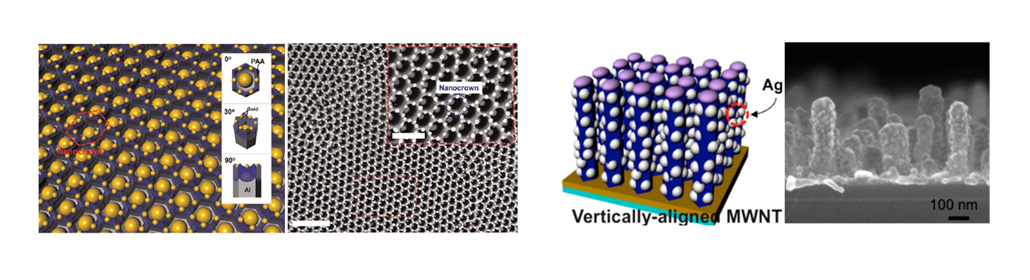
Plasmonic nanostructures in our group
In our group, we are trying to fabricate large-area uniform and cost-effective plasmonic nanostructures. We mainly utilize a template-based nanolithography where large-area periodic nanotemplates such as AAO, ZnO nanorods, and graphene are used and evaporation process of metal is followed. The LSPR positions of plasmonic nanostructures could be controlled by adjusting the morpholgical properties (ex. the pore size and the length of nanorods) of nanotemplates and the thickness of evaporated metals. Furthermore, post-treatment process such as annealing could change arrangement of plasmonic nanoparticles.
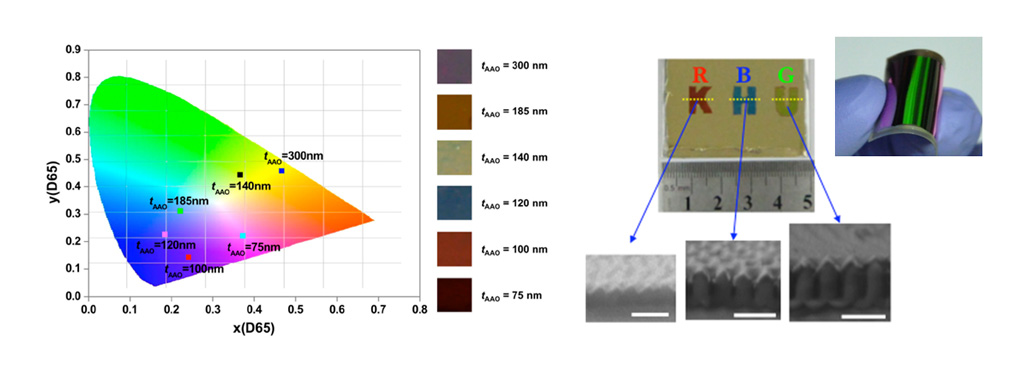
- Nanoplasmonic applicationsNanoplasmonic color
The color is related with light-matter interaction. Basically, materials absorb specific wavelength of light that can excite electrons in materials. So, the specific color is determined by absorption property of materials in macroscale. In nanoscale, the optical properties are decided by both material and systematic properties. In other words, we can control the colors by changing optical components related with interference or structural specification such as dimension, shape of novel materials and geometrical properties of dielectric layer. Based on these design variables, we study plasmonic color filters and active plasmonic color sensors.
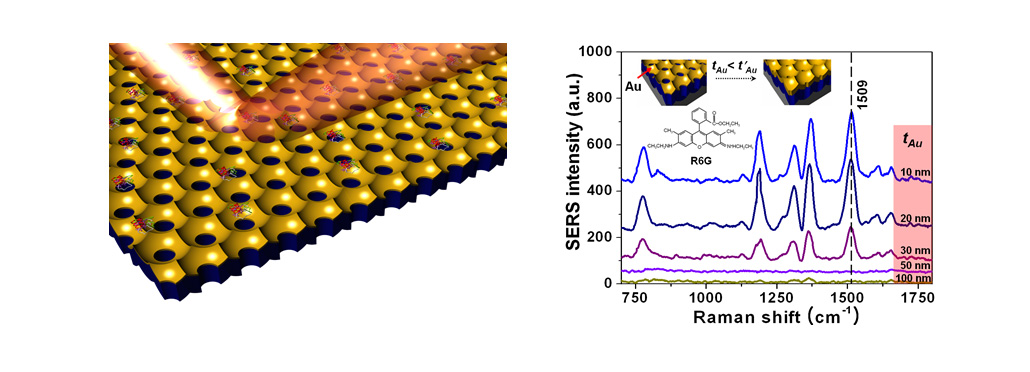
Plasmonic molecular sensors
Raman scattering is the inelastic scattering of a photon by molecules which are excited to higher vibrational or rotational energy levels. We can obtain the molecular information such as chemical binding state and composition using Raman scattering analysis without physical damage on samples. However, the intensity is too low to fully analyze target materials. Therefore, we investigate surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to overcome the limitation of conventional Raman spectroscopy with plasmonic nanostructures. We can use the SERS technique to analyze various materials or biological molecules.